Page 78 - Haryana Water Resources Atlas 2025
P. 78
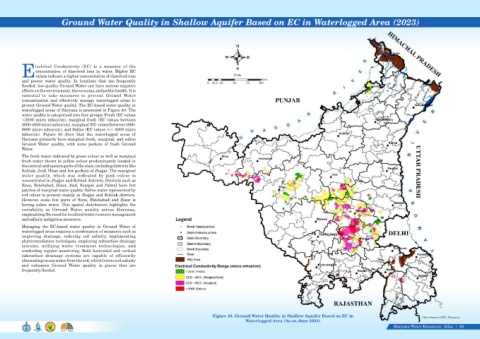
Ground Water Quality in Shallow Aquifer Based on EC in Waterlogged Area (2023)
N
W E
lectrical Conductivity (EC) is a measure of the
concentration of dissolved ions in water. Higher EC S
Evalues indicate a higher concentration of dissolved ions Scale
and poorer water quality. In locations that are frequently Kms
0 12.5 25 50 75 100
flooded, low-quality Ground Water can have serious negative
effects on the environment, the economy, and public health. It is
essential to take measures to prevent Ground Water
contamination and effectively manage waterlogged areas to
protect Ground Water quality. The EC-based water quality in
waterlogged areas of Haryana is presented in Figure 40. The
water quality is categorized into four groups: Fresh (EC values
<2000 micro mhos/cm), marginal fresh (EC values between
2000-4000 micro mhos/cm), marginal (EC values between 4000-
6000 micro mhos/cm), and Saline (EC values >= 6000 micro
mhos/cm). Figure 40 show that the waterlogged areas of
Haryana primarily have marginal fresh, marginal, and saline
Ground Water quality, with some pockets of fresh Ground
Water.
The fresh water indicated by green colour as well as marginal
fresh water shown in yellow colour predominantly located in
the central and eastern parts of the state, including districts like
Rohtak, Jind, Hisar and few pockets of Jhajjar. The mariginal
water quality, which was indicated by pink colour is
concentrated in Jhajjar and Rohtak districts. Districts such as
Sirsa, Fatehabad, Hisar, Jind, Sonipat and Palwal have few
patches of marginal water quality. Saline water represented by
red colour is present mainly in Jhajjar and Rohtak districts.
However, some few parts of Sirsa, Fatehabad and Hisar is
having saline water. This spatial distribution highlights the
variability in Ground Water quality across Haryana,
emphasizing the need for localized water resource management
and salinity mitigation measures.
Managing the EC-based water quality in Ground Water of
waterlogged areas requires a combination of measures such as
improving drainage, reducing soil salinity, implementing
phytoremediation techniques, employing subsurface drainage
systems, utilizing water treatment technologies, and
conducting regular monitoring. Both horizontal and vertical
subsurface drainage systems are capable of efficiently
eliminating excess water from the soil, which lowers soil salinity
and enhances Ground Water quality in places that are
frequently flooded.
Figure 40. Ground Water Quality in Shallow Aquifer Based on EC in Data Source-GWC, Haryana
Waterlogged Area (As on June 2023)
Haryana Water Resources Atlas 60|