Page 83 - Haryana Water Resources Atlas 2025
P. 83
Stage of Ground Water Extraction Categorization (2024)
he "Stage of Ground Water Extraction" is a measure that represents the ratio N
of "Annual Ground Water Extraction" to "Annual Extractable Ground Water
TResource," typically expressed as a percentage. This parameter is essential W E
in hydrogeology for assessing and monitoring the extent of Ground Water
extraction from an aquifer or specific region. It helps in managing Ground Water S
depletion, planning future water supply, identifying places with problems with
Ground Water quality, and pinpointing areas where excessive Ground Water Scale
removal occurs. The block-wise stage of Ground Water extraction in Haryana is Kms
0 12.5 25 50 75 100
categorized according to Ground Water development as of 2023, as shown in Figure
43. The stage of Ground Water extraction is determined by:
Existing Gross GW Extraction for all Uses
Stage of GW Extraction= ×100
Annual Extractable GW Resources
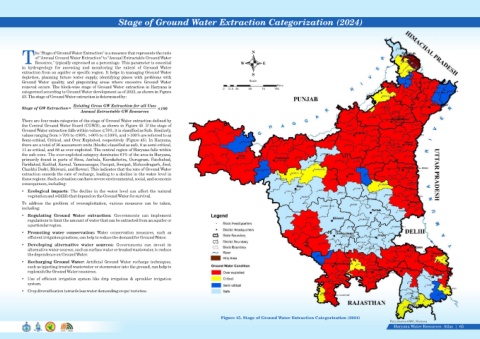
There are four main categories of the stage of Ground Water extraction defined by
the Central Ground Water Board (CGWB), as shown in Figure 45. If the stage of
Ground Water extraction falls within values ≤70%, it is classified as Safe. Similarly,
values ranging from >70% to ≤90%, >90% to ≤100%, and >100% are referred to as
Semi-critical, Critical, and Over Exploited, respectively (Figure 45). In Haryana,
there are a total of 36 assessment units (blocks) classified as safe, 8 as semi-critical,
11 as critical, and 88 as over-exploited. The central region of Haryana falls within
the safe zone. The over-exploited category dominates 61% of the area in Haryana,
primarily found in parts of Sirsa, Ambala, Kurukshetra, Gurugram, Fatehabad,
Faridabad, Kaithal, Karnal, Yamunanagar, Panipat, Sonipat, Mahendragarh, Jind,
Charkhi Dadri, Bhiwani, and Rewari. This indicates that the rate of Ground Water
extraction exceeds the rate of recharge, leading to a decline in the water level in
these regions. Such a situation can have severe environmental, social, and economic
consequences, including:
Ÿ Ecological impacts: The decline in the water level can affect the natural
vegetation and wildlife that depend on the Ground Water for survival.
To address the problem of overexploitation, various measures can be taken,
including:
Ÿ Regulating Ground Water extraction: Governments can implement
regulations to limit the amount of water that can be extracted from an aquifer or
a particular region.
Ÿ Promoting water conservation: Water conservation measures, such as
efficient irrigation practices, can help to reduce the demand for Ground Water.
Ÿ Developing alternative water sources: Governments can invest in
alternative water sources, such as surface water or treated wastewater, to reduce
the dependence on Ground Water.
Ÿ Recharging Ground Water: Artificial Ground Water recharge techniques,
such as injecting treated wastewater or stormwater into the ground, can help to
replenish the Ground Water resources.
Ÿ Use of efficient irrigation system like drip irrigation & sprinkler irrigation
system.
Ÿ Crop diversification towards less water demanding crops/ varieties.
Figure 45. Stage of Ground Water Extraction Categorization (2024)
Data Source-GWC, Haryana
Haryana Water Resources Atlas 65|