Page 86 - Haryana Water Resources Atlas 2025
P. 86
W
Water Stress / Gap (2023)ater Stress / Gap (2023)
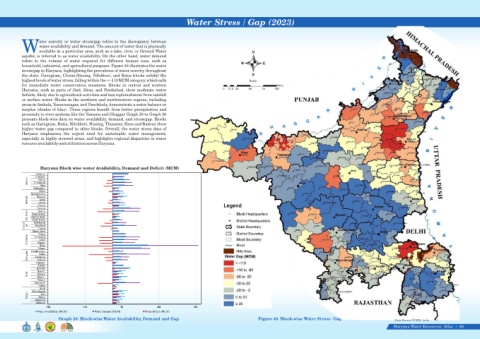
ater scarcity or water stress/gap refers to the discrepancy between
water availability and demand. The amount of water that is physically
Wavailable in a particular area, such as a lake, river, or Ground Water N
aquifer, is referred to as water availability. On the other hand, water demand
refers to the volume of water required for different human uses, such as
W E
household, industrial, and agricultural purposes. Figure 48 illustrates the water
stress/gap in Haryana, highlighting the prevalence of water scarcity throughout
the state. Gurugram, Chirao,Nissing, Nilokheri, and Ratia blocks exhibit the S
highest levels of water stress, falling within the <-110 MCM category, which calls Scale
for immediate water conservation measures. Blocks in central and western Kms
Haryana, such as parts of Jind, Sirsa, and Fatehabad, show moderate water 0 12.5 25 50 75 100
deficits, likely due to agricultural activities and less replenishment from rainfall
or surface water. Blocks in the northern and northwestern regions, including
areas in Ambala, Yamunanagar, and Panchkula, demonstrate a water balance or
surplus (shades of blue). These regions benefit from better precipitation and
proximity to river systems like the Yamuna and Ghaggar Graph 28 to Graph 30
presents block-wise data on water availability, demand, and stress/gap. Blocks
such as Gurugram, Ratia, Nilokheri, Nissing, Thanesar, Sirsa and Radour show
higher water gap compared to other blocks. Overall, the water stress data of
Haryana emphasizes the urgent need for sustainable water management,
especially in highly stressed areas, and highlights regional disparities in water
resource availability and utilization across Haryana.
Haryana Block wise water Availability, Demand and Deficit (MCM)
Graph 28. Block-wise Water Availability, Demand and Gap Figure 48. Block-wise Water Stress / Gap (2023) Data Source-CGWB, India
Haryana Water Resources Atlas 68|