Page 134 - Haryana Water Resources Atlas 2025
P. 134
Salt Affected Areas (2023)
alt-affected areas are regions where the soil has become saline due to the
accumulation of salts, often caused by inadequate drainage and/or excessive
SGround Water usage for irrigation. This salt accumulation can lead to soil
degradation, reduced crop yields, and even land abandonment. Salt-affected places are N
found all over the world, although they are more common in arid and semi-arid locations
where it is difficult to remove excess salt from the soil due to high rates of evaporation and W E
little rainfall. The northwest and western regions of India, which include Punjab,
Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Uttar Pradesh, are primarily affected by salt.
S
Haryana, in particular, faces significant challenges with salt-affected land, especially in Scale
districts such as Bhiwani, Hisar, Jhajjar, and Sirsa. These areas experience high Kms
evaporation rates and low rainfall, which contribute to salt accumulation in the soil. 0 12.5 25 50 75 100
Improper irrigation practices, inadequate drainage, and excessive Ground Water
extraction exacerbate the situation. Therefore, mapping the spatial distribution of salt-
affected areas in Haryana is crucial for effective soil and water resource management.
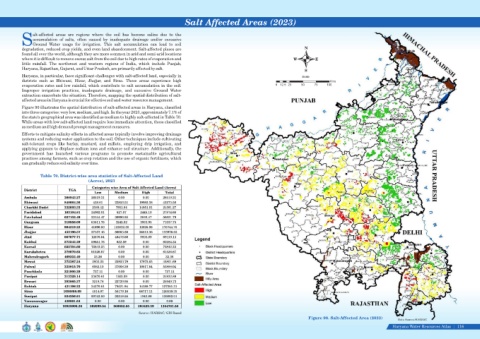
Figure 90 illustrates the spatial distribution of salt-affected areas in Haryana, classified
into three categories: very low, medium, and high. In the year 2023, approximately 7.1% of
the state's geographical area was identified as medium to highly salt-affected in Table 70.
While areas with low salt-affected land require less immediate attention, those classified
as medium and high demand prompt management measures.
Efforts to mitigate salinity effects in affected areas typically involve improving drainage
systems and reducing water application to the soil. Other techniques include cultivating
salt-tolerant crops like barley, mustard, and millets, employing drip irrigation, and
applying gypsum to displace sodium ions and enhance soil structure. Additionally, the
government has launched various programs to promote sustainable agricultural
practices among farmers, such as crop rotation and the use of organic fertilizers, which
can gradually reduce soil salinity over time.
Table 70. District-wise area statistics of Salt-Affected Land
(Acres), 2023
Source: HARSAC/ GIS Based
Figure 90. Salt-Affected Area (2023)
Data Source-HARSAC
Haryana Water Resources Atlas 116|