Page 119 - Haryana Water Resources Atlas 2025
P. 119
Productivity of Rabi Crops (2022-2023)
N
rop productivity is the amount of crops produced in a certain amount of time per
unit of land. It functions as a gauge for the effectiveness and efficacy of agricultural W E
Ctechniques used in crop cultivation. The productivity of crops is influenced by
various factors, including soil quality, climate, water availability, fertilizer and pesticide S
usage, plant genetics, and management techniques. In Haryana, the productivity of Rabi
Scale
crops varies annually and is primarily dependent on these factors. Nevertheless, the
Kms
state's favorable soil and climate allow it to continually yield large amounts of Rabi crops. 0 12.5 25 50 75 100
Crop productivity plays a vital role in ensuring food security, generating income for
farmers, and contributing to overall economic growth.
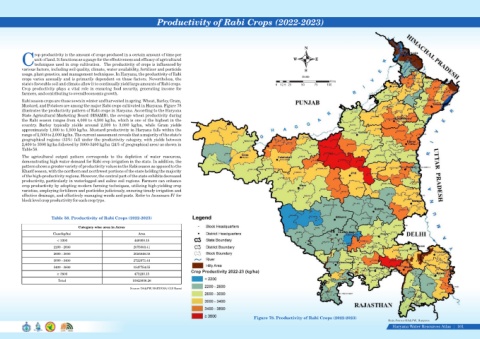
Rabi season crops are those sown in winter and harvested in spring. Wheat, Barley, Gram,
Mustard, and Potatoes are among the major Rabi crops cultivated in Haryana. Figure 78
illustrates the productivity pattern of Rabi crops in Haryana. According to the Haryana
State Agricultural Marketing Board (HSAMB), the average wheat productivity during
the Rabi season ranges from 4,000 to 4,500 kg/ha, which is one of the highest in the
country. Barley typically yields around 2,500 to 3,000 kg/ha, while Gram yields
approximately 1,000 to 1,500 kg/ha. Mustard productivity in Haryana falls within the
range of 1,500 to 2,000 kg/ha. The current assessment reveals that a majority of the state's
geographical regions (33%) fall under the productivity category, with yields between
2,600 to 3000 kg/ha followed by 3000-3400 kg/ha (24% of geographical area) as shown in
Table 58.
The agricultural output pattern corresponds to the depletion of water resources,
demonstrating high water demand for Rabi crop irrigation in the state. In addition, the
pattern shows a greater variety of productivity values in the Rabi season as opposed to the
Kharif season, with the northern and northwest portions of the state holding the majority
of the high-productivity regions. However, the central part of the state exhibits decreased
productivity, particularly in waterlogged and saline soil regions. Farmers can enhance
crop productivity by adopting modern farming techniques, utilizing high-yielding crop
varieties, employing fertilizers and pesticides judiciously, ensuring timely irrigation and
effective drainage, and effectively managing weeds and pests. Refer to Annexure-IV for
block level crop productivity for each crop type.
Table 58. Productivity of Rabi Crops (2022-2023)
Category wise area in Acres
Class(kg/ha) Area
< 2200 449200.15
2200 - 2600 2075003.41
2600 - 3000 3656846.58
3000 - 3400 2722971.43
3400 - 3800 1547754.55
Crop Productivity 2022-23 (kg/ha)
≥ 3800 473230.15
Total 10925006.26
Source: DA&FW, HARYANA/ GIS Based
Figure 78. Productivity of Rabi Crops (2022-2023)
Data Source-DA&FW, Haryana
Haryana Water Resources Atlas 101|