Page 106 - Haryana Water Resources Atlas 2025
P. 106
Distribution of Sugarcane during Kharif Season (2023)
ugarcane, a tall and perennial grass belonging to the genus Saccharum and N
tribe Andropogoneae, is a valuable crop used for sugar, ethanol, and paper
Sproduction, making it a significant cash crop. Despite Haryana's suboptimal W E
climatic conditions for intensive sugarcane cultivation due to temperature
variations, mapping its cultivation is crucial as it holds economic importance in the
S
country. Sugarcane is an ecologically sustainable renewable agricultural resource
that yields sugar, fiber, biofuel, fertilizer, and a variety of byproducts. Its juice is Scale
used to make jaggery (gur), white sugar, and brown sugar (khandsari). Typically, Kms
0 12.5 25 50 75 100
sugarcane is sown during the kharif season (monsoon season) from June to July
and harvested in the winter season from December to January. Some farmers also
plant sugarcane after wheat harvesting, typically in April to mid-May.
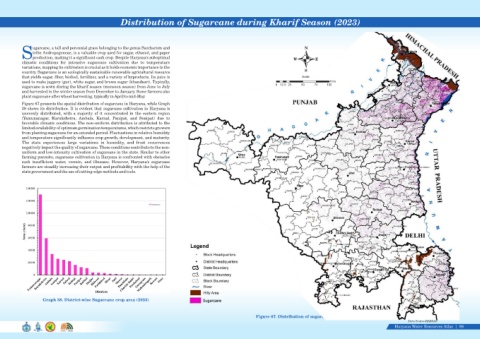
Figure 67 presents the spatial distribution of sugarcane in Haryana, while Graph
38 shows its distribution. It is evident that sugarcane cultivation in Haryana is
unevenly distributed, with a majority of it concentrated in the eastern region
(Yamunanagar, Kurukshetra, Ambala, Karnal, Panipat, and Sonipat) due to
favorable climatic conditions. The non-uniform distribution is attributed to the
limited availability of optimum germination temperatures, which restricts growers
from planting sugarcane for an extended period. Fluctuations in relative humidity
and temperature significantly influence crop growth, development, and maturity.
The state experiences large variations in humidity, and frost occurrences
negatively impact the quality of sugarcane. These conditions contribute to the non-
uniform and low-intensity cultivation of sugarcane in the state. Similar to other
farming pursuits, sugarcane cultivation in Haryana is confronted with obstacles
such insufficient water, vermin, and illnesses. However, Haryana's sugarcane
farmers are steadily increasing their output and profitability with the help of the
state government and the use of cutting-edge methods and tools.
Graph 38. District-wise Sugarcane crop area (2023)
Figure 67. Distribution of sugarcane during Kharif season (2023)
Data Source-HARSAC
Haryana Water Resources Atlas 88|