Page 111 - Haryana Water Resources Atlas 2025
P. 111
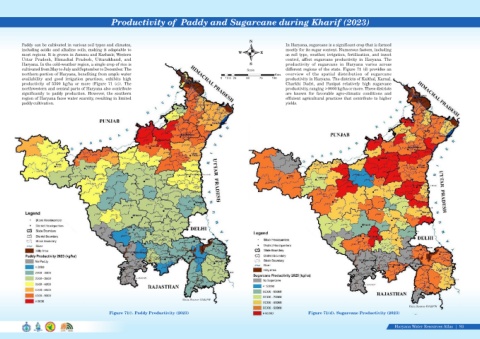
Productivity of Paddy and Sugarcane during Kharif (2023)
N
Paddy can be cultivated in various soil types and climates, In Haryana, sugarcane is a significant crop that is farmed
including acidic and alkaline soils, making it adaptable to mostly for its sugar content. Numerous factors, including
most regions. It is grown in Jammu and Kashmir, Western W E as soil type, weather, irrigation, fertilization, and insect
Uttar Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and control, affect sugarcane productivity in Haryana. The
Haryana. In the cold-weather region, a single crop of rice is S productivity of sugarcane in Haryana varies across
cultivated from May to July and September to December. The Scale different regions of the state. Figure 71 (d) provides an
northern portion of Haryana, benefiting from ample water Kms overview of the spatial distribution of sugarcane
availability and good irrigation practices, exhibits high 0 12.5 25 50 75 100 productivity in Haryana. The districts of Kaithal, Karnal,
productivity of 5500 kg/ha or more (Figure 71 (c)). The Charkhi Dadri, and Panipat relatively high sugarcane
northwestern and central parts of Haryana also contribute productivity, ranging >9000 kg/ha or more. These districts
significantly to paddy production. However, the southern are known for favorable agro-climatic conditions and
region of Haryana faces water scarcity, resulting in limited efficient agricultural practices that contribute to higher
paddy cultivation. yields.
Data Source-DA&FW
Data Source-DA&FW
Figure 71©. Paddy Productivity (2023) Figure 71(d). Sugarcane Productivity (2023)
Haryana Water Resources Atlas 93|