Page 36 - Haryana Water Resources Atlas 2025
P. 36
Drainage Density
N
W E
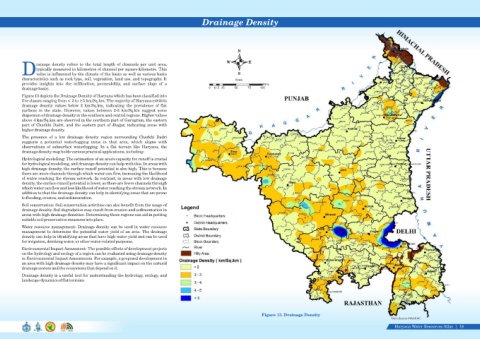
rainage density refers to the total length of channels per unit area,
typically measured in kilometres of channel per square kilometre. This
Dvalue is influenced by the climate of the basin as well as various basin S
characteristics such as rock type, soil, vegetation, land use, and topography. It Scale
provides insights into the infiltration, permeability, and surface slope of a Kms
drainage basin. 0 12.5 25 50 75 100
Figure 13 depicts the Drainage Density of Haryana which has been classified into
five classes ranging from < 2 to ≥5 km/Sq.km. The majority of Haryana exhibits
drainage density values below 2 km/Sq.km, indicating the prevalence of flat
surfaces in the state. However, values between 2-3 km/Sq.km suggest some
dispersion of drainage density in the southern and central regions. Higher values
above 4 km/Sq.km are observed in the northern part of Gurugram, the eastern
part of Charkhi Dadri, and the eastern part of Jhajjar, indicating areas with
higher drainage density.
The presence of a low drainage density region surrounding Charkhi Dadri
suggests a potential waterlogging issue in that area, which aligns with
observations of subsurface waterlogging. In a flat terrain like Haryana, the
drainage density map holds various practical applications, including:
Hydrological modelling: The estimation of an area's capacity for runoff is crucial
for hydrological modelling, and drainage density can help with this. In areas with
high drainage density, the surface runoff potential is also high. This is because
there are more channels through which water can flow, increasing the likelihood
of water reaching the stream network. In contrast, in areas with low drainage
density, the surface runoff potential is lower, as there are fewer channels through
which water can flow and less likelihood of water reaching the stream network. In
addition to that the drainage density can help in identifying areas that are prone
to flooding, erosion, and sedimentation.
Soil conservation: Soil conservation activities can also benefit from the usage of
drainage density. Soil degradation may result from erosion and sedimentation in
areas with high drainage densities. Determining these regions can aid in putting
suitable soil preservation measures into place.
Water resource management: Drainage density can be used in water resource
management to determine the potential water yield of an area. The drainage
density can help in identifying areas that have high water yield and can be used
for irrigation, drinking water, or other water-related purposes.
Environmental Impact Assessment: The possible effects of development projects
on the hydrology and ecology of a region can be evaluated using drainage density
in Environmental Impact Assessments. For example, a proposed development in
an area with high drainage density may have a significant impact on the natural
drainage system and the ecosystems that depend on it.
Drainage density is a useful tool for understanding the hydrology, ecology, and
landscape dynamics of flat terrains.
Figure 13. Drainage Density
Data Source-HARSAC
Haryana Water Resources Atlas 18|